The Covid-19 pandemic has brought into sharp focus how crucial keeping active is to halt deconditioning amongst older adults.
— Chartered Society of Physiotherapy (@thecsp) October 1, 2020
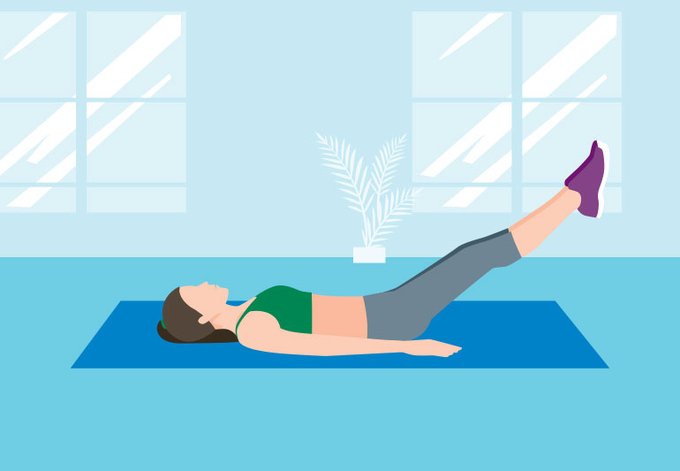
Help us share 6 simple exercises from physiotherapists to help build strength and balance for older people. https://t.co/mlSLVv3c4q #OlderPeoplesDay pic.twitter.com/QfXZSzvsyM








 Mayo Clinic Sports
Mayo Clinic Sports