
Decision Fatigue is real and you’re not alone – Anna Mathur @motherandbaby





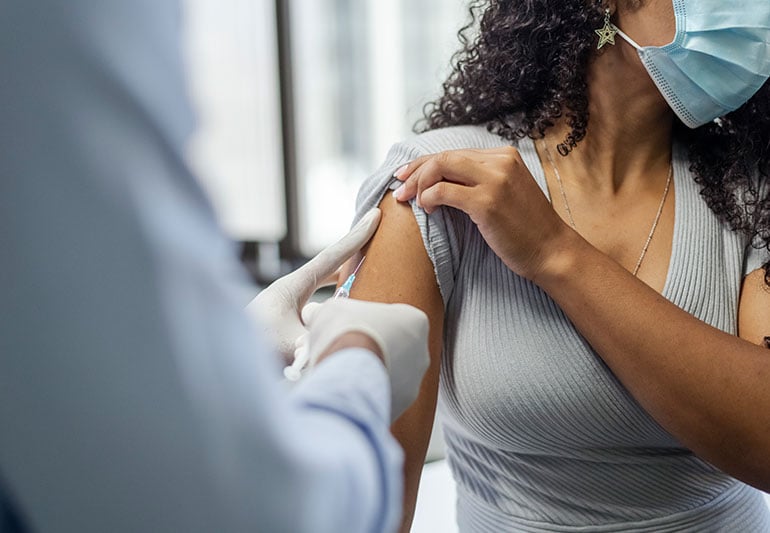
Healthcare providers across the country are bracing for another season of treating respiratory viruses like the flu, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and COVID-19.
And while the flu might not seem like something to worry about, it’s a virus we should all be prepared for. So, you may be wondering, Should I get a flu shot?
“Influenza is a very serious disease, and during a normal flu season, around 40,000 or more people die from it,” says infectious disease specialist Kristin Englund, MD. “So, with any preventable disease, we should do everything we can to protect ourselves.”
Getting your flu vaccine is vital to not just keeping you and your family healthy, but also relieving our over-burdened healthcare system.
To learn more about the importance of getting the flu vaccine, we talked to Dr. Englund, along with infectious disease clinical pharmacist Kaitlyn Rivard, PharmD.
First of all, Dr. Englund notes that it’s just good practice to get a flu shot every year. She adds that the vaccine’s prevention-geared properties are key.
“When people get influenza or get the flu, it’s not only just the symptoms that they have, like a cough, fever and an infection in the lungs,” she says. “It taxes the body and really puts a lot of stress on all of the other systems.”
That can cause some serious complications, she continues. “You can have a heart attack or even a stroke as a side effect from having influenza. So, we want to make sure that we’re keeping everybody healthy from all of these complications.”
Dr. Englund says that a flu shot is especially important this year because other respiratory viruses like COVID-19 and RSV will be circulating.
“We’re going to have influenza, RSV and COVID-19 coexisting and there’s a lot of overlap between the symptoms,” she states. “We also anticipate that there will be some people who have co-infections, which could be difficult.”
We bet you’re now wondering: So, when should I get a flu shot?
Dr. Englund and Dr. Rivard advise getting a flu vaccine as soon as it becomes available. Many healthcare providers, including the Cleveland Clinic, begin offering the flu vaccine at the beginning of September.
And in case you were wondering, the flu vaccine doesn’t interfere with the COVID-19 vaccine or the RSV vaccine.
“All available COVID-19 and RSV vaccines can be given at the same time as the flu vaccine,” clarifies Dr. Rivard. “If someone is coming in for their flu shot and they’re eligible for a COVID-19 vaccine or RSV vaccine but haven’t received it yet, we can offer that. In fact, both the CDC [U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommend co-administering almost any two vaccines together.”
She adds that there are very few instances in which certain vaccines can’t be administered at the same time, noting that children often receive multiple vaccines during one visit to their pediatrician.
And there’s no concern about overloading our immune systems with multiple vaccines.
“We’re exposed to things that stimulate our immune system all the time,” Dr. Englund says. “Our immune system is constantly responding to various exposures even if you don’t realize it.”
One reason it’s so important to get your annual flu shot is this: Protecting yourself is a lot easier than treating the flu.
“There are some treatments available for the flu that are evolving,” Dr. Englund says. “But to avoid the disease altogether or to only have a mild case because you’ve been vaccinated is much better than trying to treat it. Prevention is best.”
And that goes equally for kids — it’s also crucial to get them vaccinated for the flu.
“It’s important for children to get the flu vaccine, too, because the circulation of flu in children, if nothing else, puts adults at risk, too,” emphasizes Dr. Englund.
“Influenza is a serious disease and it’s unpredictable, and otherwise healthy children are unfortunately hospitalized and die every year because of it. So, even for normal, healthy children, it’s really important to get vaccinated every year.”

Why not try your hand at making homemade tomato sauce? The freshness of the tomatoes and the smokiness of the roasted vegetables make this a great topping for spaghetti. If you don’t have your own garden, use canned Roma tomatoes for a tasty dish that includes roasted mushrooms, broccoli and peppers.
Tomato sauce
Olive oil cooking spray
2 garlic cloves, minced
1 small carrot, minced
1 shallot, minced
4 cups peeled, seeded, and diced ripe tomatoes or one 28-ounce can no-salt-added diced tomatoes, drained
1/4 cup dry red wine
1 1/2 tablespoons balsamic vinegar
1/4 teaspoon crushed red pepper flakes, optional
1/4 cup chopped fresh basil
Pasta
1/2 pound whole wheat spaghetti
3/4 pound broccoli florets and stalks, peeled and cut into bite-size pieces
2 portobello mushrooms, halved and thinly sliced
1 red, yellow or orange bell pepper, seeded and coarsely chopped
1 1/2 tablespoons extra-virgin olive oil
1 1/2 tablespoons balsamic vinegar
Freshly grated pepper
2 tablespoons freshly grated Parmesan cheese
Makes 4 servings
Calories: 363
Total fat: 4 g
Protein: 15 g
Carbohydrate: 71 g
Dietary fiber: 4 g
Cholesterol: 0 mg
Sodium: 100 mg
Potassium: 93 mg
— Cleveland Clinic Healthy Heart Lifestyle Guide and Cookbook (© 2007 Broadway Books).

4 January 2023
News release
Reading time: 3 min (759 words)
The risks and harms associated with drinking alcohol have been systematically evaluated over the years and are well documented. The World Health Organization has now published a statement in The Lancet Public Health: when it comes to alcohol consumption, there is no safe amount that does not affect health.
Alcohol is a toxic, psychoactive, and dependence-producing substance and has been classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer decades ago – this is the highest risk group, which also includes asbestos, radiation and tobacco. Alcohol causes at least seven types of cancer, including the most common cancer types, such as bowel cancer and female breast cancer. Ethanol (alcohol) causes cancer through biological mechanisms as the compound breaks down in the body, which means that any beverage containing alcohol, regardless of its price and quality, poses a risk of developing cancer.
The risk of developing cancer increases substantially the more alcohol is consumed. However, latest available data indicate that half of all alcohol-attributable cancers in the WHO European Region are caused by “light” and “moderate” alcohol consumption – less than 1.5 litres of wine or less than 3.5 litres of beer or less than 450 millilitres of spirits per week. This drinking pattern is responsible for the majority of alcohol-attributable breast cancers in women, with the highest burden observed in countries of the European Union (EU). In the EU, cancer is the leading cause of death – with a steadily increasing incidence rate – and the majority of all alcohol-attributable deaths are due to different types of cancers.
To identify a “safe” level of alcohol consumption, valid scientific evidence would need to demonstrate that at and below a certain level, there is no risk of illness or injury associated with alcohol consumption. The new WHO statement clarifies: currently available evidence cannot indicate the existence of a threshold at which the carcinogenic effects of alcohol “switch on” and start to manifest in the human body.
Moreover, there are no studies that would demonstrate that the potential beneficial effects of light and moderate drinking on cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes outweigh the cancer risk associated with these same levels of alcohol consumption for individual consumers.
“We cannot talk about a so-called safe level of alcohol use. It doesn’t matter how much you drink – the risk to the drinker’s health starts from the first drop of any alcoholic beverage. The only thing that we can say for sure is that the more you drink, the more harmful it is – or, in other words, the less you drink, the safer it is,” explains Dr Carina Ferreira-Borges, acting Unit Lead for Noncommunicable Disease Management and Regional Advisor for Alcohol and Illicit Drugs in the WHO Regional Office for Europe.
Despite this, the question of beneficial effects of alcohol has been a contentious issue in research for years.
“Potential protective effects of alcohol consumption, suggested by some studies, are tightly connected with the comparison groups chosen and the statistical methods used, and may not consider other relevant factors”, clarifies Dr Jürgen Rehm, member of the WHO Regional Director for Europe’s Advisory Council for Noncommunicable Diseases and Senior Scientist at the Institute for Mental Health Policy Research and the Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, Canada.
Globally, the WHO European Region has the highest alcohol consumption level and the highest proportion of drinkers in the population. Here, over 200 million people in the Region are at risk of developing alcohol-attributable cancer.
Disadvantaged and vulnerable populations have higher rates of alcohol-related death and hospitalization, as harms from a given amount and pattern of drinking are higher for poorer drinkers and their families than for richer drinkers in any given society.
“So, when we talk about possible so-called safer levels of alcohol consumption or about its protective effects, we are ignoring the bigger picture of alcohol harm in our Region and the world. Although it is well established that alcohol can cause cancer, this fact is still not widely known to the public in most countries. We need cancer-related health information messages on labels of alcoholic beverages, following the example of tobacco products; we need empowered and trained health professionals who would feel comfortable to inform their patients about alcohol and cancer risk; and we need overall wide awareness of this topic in countries and communities,” adds Dr Ferreira-Borges.

Today is #WorldHeartDay, and we are shining a light on proactive cardiac health.
Professor Pat Nash, Consultant Cardiologist at Blackrock Health, explains the types of screening tests available for heart disease.
Professor Nash always checks key factors like smoking, diet, weight, lifestyle, exercise, and blood pressure. If there’s a strong family history, a CT Calcium Score – a powerful tool for gaining deeper insights and guiding personalised prevention strategies – might be recommended for more detail.
Knowing your risks is key to a healthy heart. Explore our cardiology services and advanced screening options: https://ow.ly/M2Fu50WP841
#IrishHeartMonth#WorldHeartDay#HeartHealth#HeartScreening#PreventativeCare#BlackrockHealth#BlackrockHealthyHeart

Some have called bananas “nature’s perfect snack,” and it’s easy to see why. The curvy yellow fruits come conveniently packaged, travel well in a lunch bag or purse and are incredibly versatile. They make a great smoothie mixer or a tasty topper on cereal or oatmeal and even have their very own category of (delicious!) muffins and bread.
“Absolutely,” says registered dietitian Elyse Homan, RD, LD. “They’re full of nutrients and easy on the gut. Very few people have problems digesting bananas.”
So, what are you eating when you peel and enjoy? A medium-sized ripe banana contains:
From vitamins to minerals to fiber, bananas are good for you, with lots of nutrition to offer. Plus, they’re easy to digest, reiterates Homan. Here’s a breakdown of banana’s most notable nutritional benefits:
With 3 grams (g) of fiber, a banana supplies nearly 10% of what you need in a day, based on a 2,000-calorie daily diet, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) dietary guidelines.
You hear “fiber” and probably automatically think of digestion. It’s true — fiber is great for your gut. It helps keep things moving in your intestines, and most of us probably need to eat more.
But fiber also impacts your health in other ways. Researchers who looked at data from nearly 200 studies found that people who ate 25 to 29 g of fiber a day had up to a 30% decreased risk of:
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is a nutrient that helps your body absorb iron and boosts your immune system’s ability to fight illness. Adults need 75 to 90 milligrams (mg) per day. A banana delivers about 10 mg of vitamin C.
Vitamin C is one of many antioxidants you can get from food. Antioxidants are important because they cancel out free radicals in your body. Free radicals can build up and damage your cells, leading to disease. But antioxidants like vitamin C keep free radicals in check.
Your body needs vitamin B6 for:
“One banana will give you one-quarter to one-third of the vitamin B6 you need in a day,” says Homan.
The USDA recommended daily intake of potassium for adults is 4,700 to 5,000 mg. A banana supplies you with about 422 mg, or a little less than 10% of what you need per day.
Potassium, a mineral, does a lot for your body. It’s essential for the proper function of your:
Getting enough potassium also keeps your blood pressure in a healthy range. Potassium, which lowers blood pressure, balances out sodium, which raises blood pressure.
Homan says potassium also benefits your vascular system — the network of blood vessels and lymph vessels that run through your body’s tissues and organs — and reduces your risk of:
A single medium-sized banana offers about 32 mg of the mineral magnesium, which fulfills around 8% to 10% of your daily magnesium requirement.
Magnesium is involved in many processes in your body, including:
Green, or unripe, bananas are high in resistant starch. “Your body can’t digest resistant starch,” notes Homan. “Instead, it’s a prebiotic that promotes the growth of good bacteria in your colon.” Prebiotics improve digestive health and can be helpful if you’re experiencing diarrhea.
“I often hear patients say they avoid bananas since they’ve heard the fruit is too high in sugar,” says Homan. As bananas ripen, much of the resistant starch changes to sugar. But the health benefits of antioxidants and fiber outweigh the naturally occurring sugar. For those worried about blood sugar levels, pair bananas with a protein source such as peanut butter or a cheese stick for better control.
A small word of warning about unripe bananas: “If you’re not used to eating resistant starch, start slowly to let your body get used to it. Some people can experience constipation, gas and bloating at first,” adds Homan.
Another plus of this fruit? In addition to all the health benefits of bananas, they’re less expensive than many other fruits.


4 January 2023
News release
Reading time: 3 min (759 words)
The risks and harms associated with drinking alcohol have been systematically evaluated over the years and are well documented. The World Health Organization has now published a statement in The Lancet Public Health: when it comes to alcohol consumption, there is no safe amount that does not affect health.
Alcohol is a toxic, psychoactive, and dependence-producing substance and has been classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer decades ago – this is the highest risk group, which also includes asbestos, radiation and tobacco. Alcohol causes at least seven types of cancer, including the most common cancer types, such as bowel cancer and female breast cancer. Ethanol (alcohol) causes cancer through biological mechanisms as the compound breaks down in the body, which means that any beverage containing alcohol, regardless of its price and quality, poses a risk of developing cancer.
The risk of developing cancer increases substantially the more alcohol is consumed. However, latest available data indicate that half of all alcohol-attributable cancers in the WHO European Region are caused by “light” and “moderate” alcohol consumption – less than 1.5 litres of wine or less than 3.5 litres of beer or less than 450 millilitres of spirits per week. This drinking pattern is responsible for the majority of alcohol-attributable breast cancers in women, with the highest burden observed in countries of the European Union (EU). In the EU, cancer is the leading cause of death – with a steadily increasing incidence rate – and the majority of all alcohol-attributable deaths are due to different types of cancers.
To identify a “safe” level of alcohol consumption, valid scientific evidence would need to demonstrate that at and below a certain level, there is no risk of illness or injury associated with alcohol consumption. The new WHO statement clarifies: currently available evidence cannot indicate the existence of a threshold at which the carcinogenic effects of alcohol “switch on” and start to manifest in the human body.
Moreover, there are no studies that would demonstrate that the potential beneficial effects of light and moderate drinking on cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes outweigh the cancer risk associated with these same levels of alcohol consumption for individual consumers.
“We cannot talk about a so-called safe level of alcohol use. It doesn’t matter how much you drink – the risk to the drinker’s health starts from the first drop of any alcoholic beverage. The only thing that we can say for sure is that the more you drink, the more harmful it is – or, in other words, the less you drink, the safer it is,” explains Dr Carina Ferreira-Borges, acting Unit Lead for Noncommunicable Disease Management and Regional Advisor for Alcohol and Illicit Drugs in the WHO Regional Office for Europe.
Despite this, the question of beneficial effects of alcohol has been a contentious issue in research for years.
“Potential protective effects of alcohol consumption, suggested by some studies, are tightly connected with the comparison groups chosen and the statistical methods used, and may not consider other relevant factors”, clarifies Dr Jürgen Rehm, member of the WHO Regional Director for Europe’s Advisory Council for Noncommunicable Diseases and Senior Scientist at the Institute for Mental Health Policy Research and the Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, Canada.
Globally, the WHO European Region has the highest alcohol consumption level and the highest proportion of drinkers in the population. Here, over 200 million people in the Region are at risk of developing alcohol-attributable cancer.
Disadvantaged and vulnerable populations have higher rates of alcohol-related death and hospitalization, as harms from a given amount and pattern of drinking are higher for poorer drinkers and their families than for richer drinkers in any given society.
“So, when we talk about possible so-called safer levels of alcohol consumption or about its protective effects, we are ignoring the bigger picture of alcohol harm in our Region and the world. Although it is well established that alcohol can cause cancer, this fact is still not widely known to the public in most countries. We need cancer-related health information messages on labels of alcoholic beverages, following the example of tobacco products; we need empowered and trained health professionals who would feel comfortable to inform their patients about alcohol and cancer risk; and we need overall wide awareness of this topic in countries and communities,” adds Dr Ferreira-Borges.